Quick Overview: A lithium-ion battery pack refers to a complete assembly of lithium-ion cells and supporting components designed to deliver a specific voltage and capacity. Today, the term is mostly used in the context of custom battery packs for industrial, automotive, and energy storage applications.
A lithium-ion battery pack is composed of multiple battery cells, a battery management system (BMS), connecting sheets, protective circuits, and labels, all integrated through a precise assembly process. The end result is a product that meets specific customer requirements in terms of voltage, capacity, and performance.
Modern battery pack production typically takes place in specialized factories. These facilities can independently design the pack structure, electronic layout, and mechanical housing based on client specifications. Once a design is approved and prototypes are verified, the pack is manufactured, quality-checked, and delivered to the customer.

Understanding the hierarchy of lithium-ion components is essential:
Battery Cell: The fundamental unit providing 3–4 volts, depending on chemistry. Cells are the core energy storage elements.
Battery Module: A physical assembly of multiple cells that increases voltage and capacity, forming a single module.
Battery Pack: A collection of modules combined with a BMS to create a complete power unit ready for end-user applications.
Battery cells are typically classified by form factor: square prismatic, cylindrical, or lithium polymer. Each type has a different electrode packaging method to fit the design requirements.
A battery pack consists of several critical systems that work together to ensure performance and safety:
1. Battery Module
The module acts as the “heart” of the pack, storing and releasing energy as needed to power devices.
2. Mechanical Housing
The housing includes covers, trays, metal brackets, end plates, and bolts. It functions as the “skeleton,” providing structural support, vibration resistance, impact protection, and environmental sealing against dust and water.
3. Electrical System
This system includes high-voltage and low-voltage wiring harnesses, relays, and connectors. The high-voltage system distributes energy from the cells to the device, while the low-voltage system transmits signals for monitoring, control, and safety management.
4. Thermal Management System
Thermal management maintains optimal operating temperatures and prevents overheating. Methods include air cooling, liquid cooling, and phase change materials. A liquid cooling system, for example, consists of cooling plates, pipes, thermal insulation, and conductive pads, ensuring the pack remains within safe temperature limits.
5. Battery Management System (BMS)
The BMS is the “brain” of the pack. It consists of:
Cell Monitoring Unit (CMU): Measures voltage, current, and temperature of each cell, providing balancing functions.
Battery Management Unit (BMU): Evaluates CMU data and takes protective actions if abnormal conditions are detected. It manages charging and discharging, monitors temperature, and communicates warnings to the device controller and end-user.
1. Cell Selection and Matching
The first step involves sorting and matching cells with similar performance characteristics. This ensures uniform capacity, internal resistance, and voltage across the pack, laying the foundation for reliable performance and longevity.
2. Cell Assembly and Welding
Cells are positioned precisely and connected using specialized fixtures and welding equipment. The process integrates the protection circuit or BMS with the cell array, creating the initial battery pack structure. Automated machines and skilled operators work together to achieve accurate and durable connections.
3. Insulation and Testing
Once assembled, semi-finished packs are insulated to prevent short circuits. Rigorous testing is conducted, including charge-discharge cycles, internal resistance measurement, capacity verification, and safety checks. Only packs that pass these tests move forward to final assembly.
4. Packaging
The final step gives the pack a professional and durable finish. Protective casings, labeling, and packaging materials enhance appearance, portability, and safety during transport and usage. The pack undergoes a last round of inspection before being packaged for shipment to customers.
Manufacturing lithium-ion battery packs is a blend of technology, precision, and craftsmanship. From careful cell selection to assembly, testing, and packaging, every step contributes to producing safe, reliable, and high-performance battery packs. These packs provide consistent power for a wide range of applications, from renewable energy systems to electric vehicles and portable electronics.
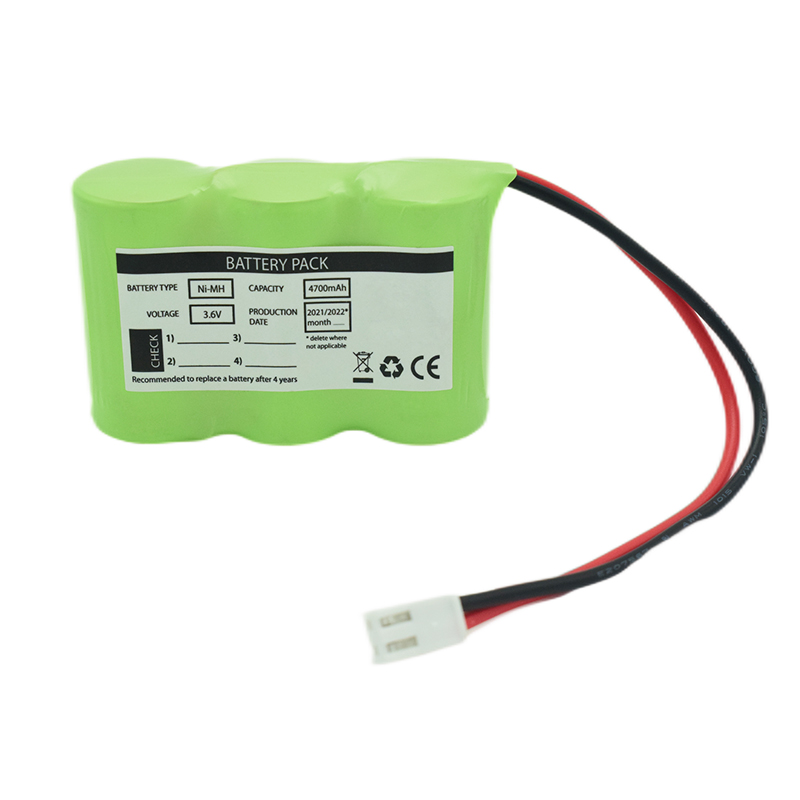
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V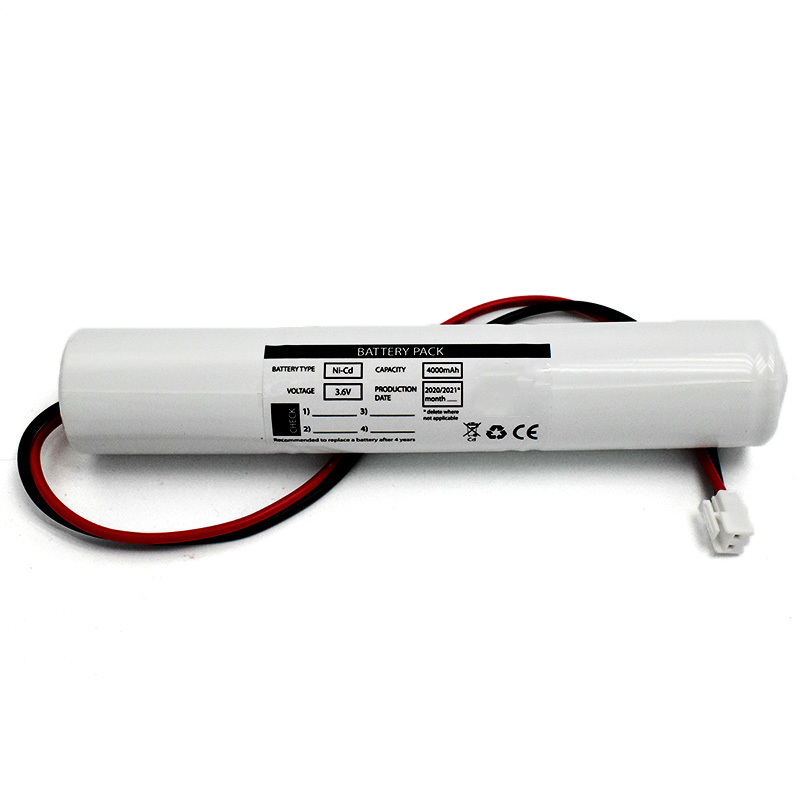 Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V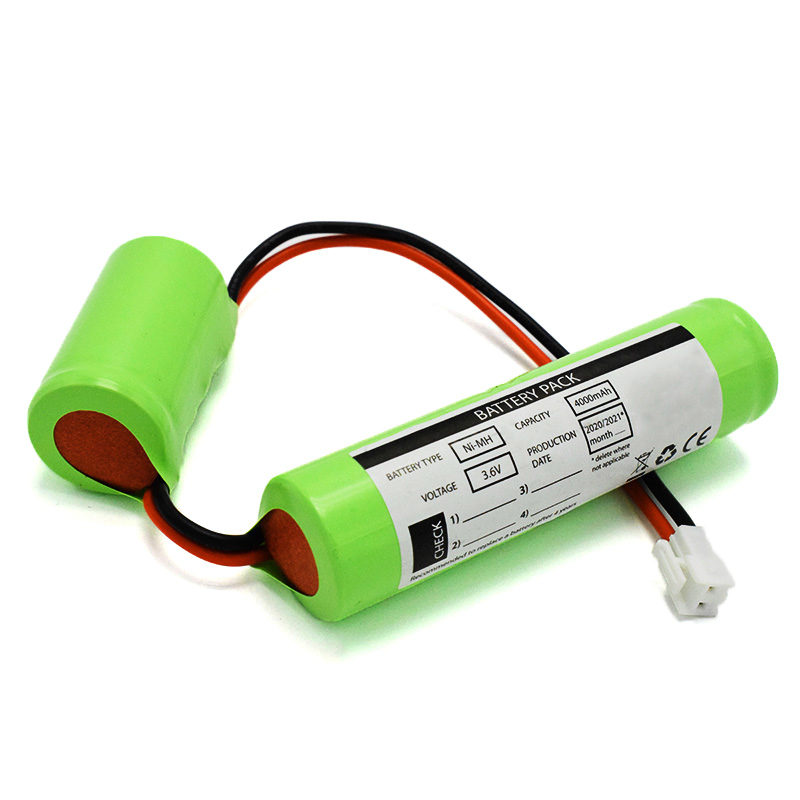 Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V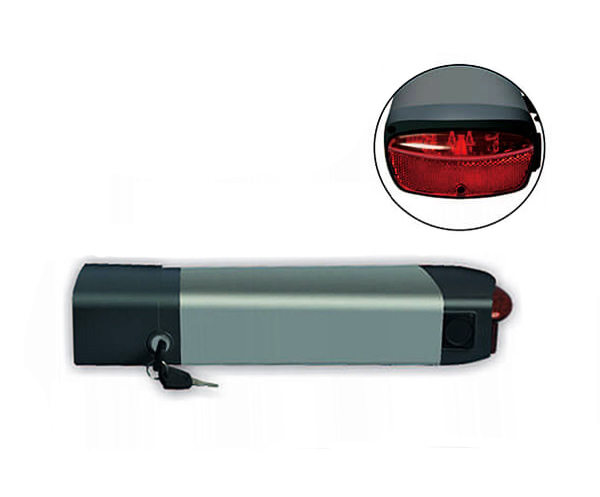 E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1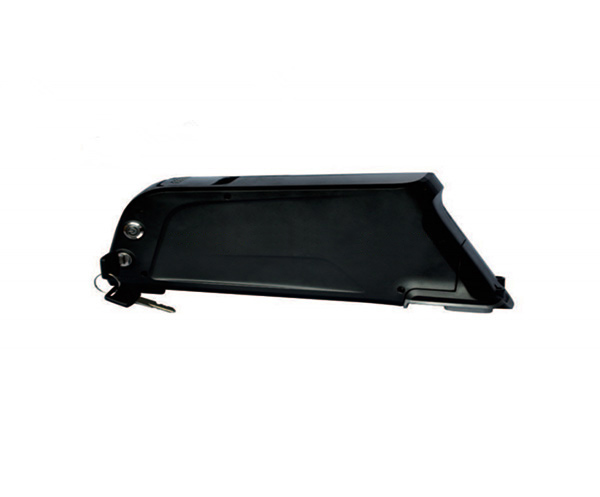 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian