A 18650 battery is a cylindrical rechargeable lithium-ion cell, named for its size — 18 mm in diameter and 65 mm in length. It’s widely used in power tools, e-bikes, laptops, flashlights, and energy storage systems due to its high energy density and stable output.
There are several types of 18650 batteries, each offering different characteristics:
Lithium Cobalt Oxide (LiCoO₂): High energy density, common in consumer electronics.
Lithium Iron Phosphate (LiFePO₄): Excellent safety, long lifespan, and thermal stability.
Lithium Manganese Oxide (LiMn₂O₄): Good temperature tolerance and discharge capability.
Depending on the application, 18650 cells can be customized for capacity, discharge rate, or temperature resistance.

A short circuit occurs when electrical current bypasses its normal path and flows directly between the positive and negative terminals with almost no resistance. This allows a massive amount of current to pass through instantly.
In a 18650 battery, short circuits can occur in two main ways:
External Short Circuit: When conductive materials like coins, tools, or wires directly connect the terminals.
Internal Short Circuit: When internal components such as separators fail or get damaged, causing the anode and cathode to touch.
Both situations are dangerous because they generate intense heat and can trigger thermal runaway.
Short circuits can result from various mechanical, environmental, or human errors. Common causes include:
Physical Impact: Dropping, crushing, or puncturing the cell may damage internal layers.
Improper Storage: Placing batteries near metal objects or in cluttered drawers.
Manufacturing Flaws: Defective separators or impurities inside the cell.
Improper Wiring: Mistakes in DIY or repair work, such as soldering without insulation.
Damaged Insulation: Worn or torn battery wraps exposing metal surfaces.
Understanding these causes helps minimize the risk of electrical accidents and equipment failure.
When a short circuit occurs, the battery undergoes a rapid and violent reaction.
Typical process:
Massive Current Flow: The circuit draws hundreds of amps almost instantly.
Extreme Heating: Internal temperatures can exceed 100°C (212°F) in seconds.
Gas Formation: The electrolyte breaks down, creating internal pressure.
Venting or Explosion: If pressure becomes too high, the battery casing can rupture.
Ignition: The released gases are flammable, increasing fire risk.
This process — known as thermal runaway — is self-sustaining and extremely hazardous once triggered.
Early detection of a short circuit can prevent catastrophic outcomes. Watch for these warning signs:
The battery gets unusually hot even when not in use.
Swelling or bulging of the casing.
Chemical or burning odor from leaked electrolyte.
Smoke or sparks coming from the cell or nearby components.
Voltage drops suddenly or fluctuates abnormally.
If you observe any of these symptoms, isolate the battery immediately in a safe, non-flammable area.
The dangers of a 18650 short circuit extend beyond the cell itself. They include:
Fire or Explosion: Flammable materials inside the cell can ignite.
Toxic Fumes: Released gases may contain harmful compounds.
Device Damage: Connected electronics or circuits may be destroyed.
Injury Risk: Burns, smoke inhalation, or debris injuries are possible.
Environmental Impact: Damaged batteries can leak pollutants if improperly discarded.
These risks underline the importance of handling lithium batteries with care and using protective mechanisms like a Battery Management System (BMS).
Preventing short circuits requires a mix of proper storage, careful handling, and quality selection.
Best practices:
Use protected cells with built-in safety circuits.
Avoid dropping, puncturing, or applying excessive force.
Store batteries in non-conductive containers away from metal objects.
Keep new and used batteries separate to prevent accidental contact.
Inspect wrapping and casings regularly for damage.
Use battery holders or cases for transport.
For battery packs, install a BMS to manage charge, balance, and temperature.
Following these steps greatly reduces the likelihood of accidental shorts and system failures.
If you suspect a short circuit or battery failure:
Disconnect the battery immediately from any circuit or device.
Move it to a safe, fire-resistant surface (such as concrete).
Do not touch or cool it with water. Allow it to cool naturally.
Avoid reuse. A shorted battery is unsafe for future operation.
Call emergency services if fire or smoke occurs.
Always treat a compromised lithium battery as hazardous material.
In most cases, no. Once a battery has shorted, it is permanently unsafe. Even if it appears functional, internal damage can lead to future failure or ignition.
Attempting to recharge or repair a shorted battery can cause:
Further internal degradation
Dangerous heating or venting
Fire hazards
Battery management circuit failure
The only safe solution is to isolate and dispose of it responsibly.
Damaged lithium batteries must never be thrown in household trash.
Safe disposal methods:
Take them to authorized recycling or hazardous waste centers.
Tape the terminals with non-conductive material to prevent contact.
Store temporarily in a fireproof container until disposal.
Responsible disposal prevents fires during transport and protects the environment from chemical leaks.
Purchase only from reliable and certified suppliers.
Keep spare cells in individual plastic cases.
Inspect for dents, leaks, or hot spots before each use.
Avoid exposing batteries to high temperatures or direct sunlight.
Use matching cells in battery packs — never mix brands or chemistries.
Choose cells with overcurrent, overcharge, and temperature protection.
Regular inspection and proper handling are key to long-term battery safety.
A short circuit in a 18650 battery can escalate rapidly into a hazardous event, leading to fire, explosion, or injury. Understanding what causes short circuits — and following preventive and emergency steps — ensures both user safety and equipment reliability.
Whether used in personal electronics, electric vehicles, or industrial systems, every 18650 battery should be treated with care. Selecting high-quality cells, using appropriate protection circuits, and handling batteries correctly are essential to maintaining safe and efficient power performance.
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V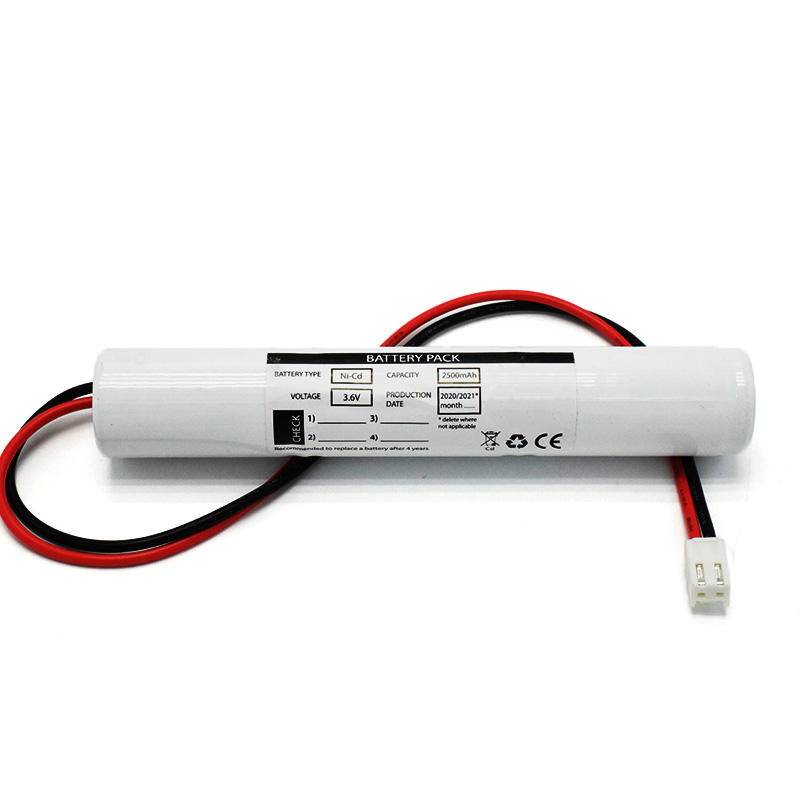 Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V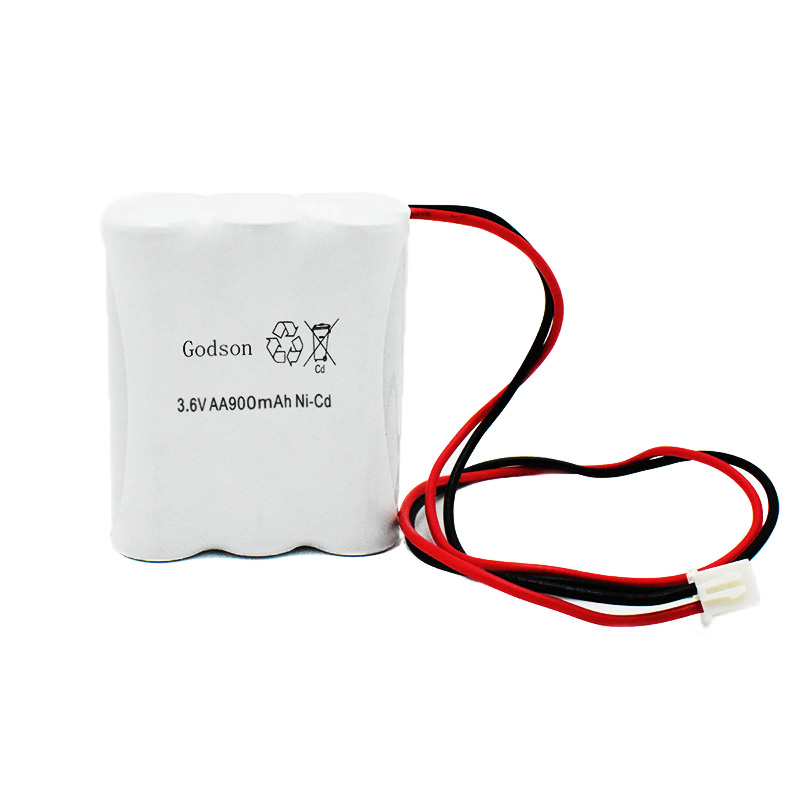 NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V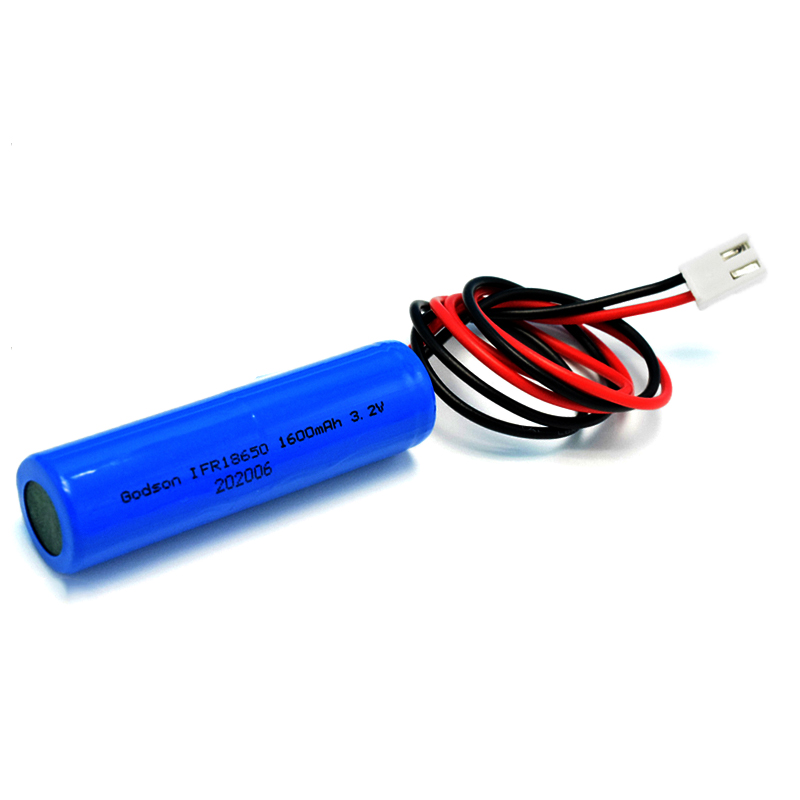 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V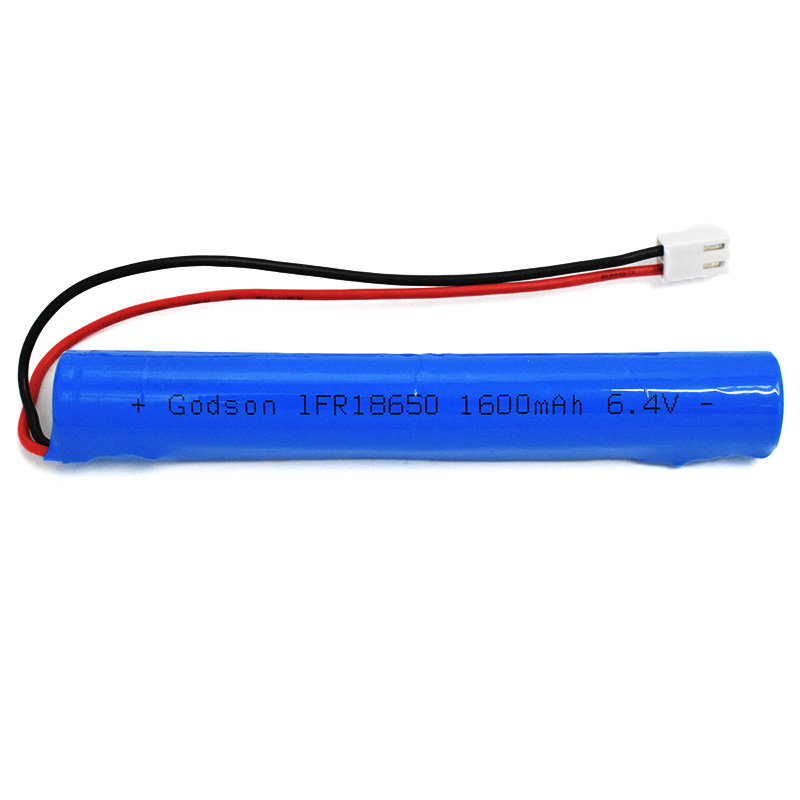 LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian