While the popularity of rechargeable batteries is often highlighted for their convenience and long-term cost savings, it’s important not to overlook the critical role primary batteries play — especially in situations where rechargeability is impractical or impossible. Alongside alkalines, primary lithium batteries are among the most widely used and indispensable battery types, especially in applications where reliability and long shelf life are essential.
From life-saving medical devices like implantable pacemakers to critical military operations and high-performance industrial tools, primary lithium cells are vital. For example, a pacemaker operating on as little as 10–20 microamperes (µA) can last 5 to 10 years before replacement is required.
In daily life, a wide range of consumer and industrial products rely on primary batteries for their simplicity and dependability — including remote controls, car key fobs, children’s toys, smart meters, vehicle pressure sensors, and digital devices. Even computer motherboards typically use CR2032 coin cells (primary lithium) to power internal memory systems where rechargeables aren’t practical.
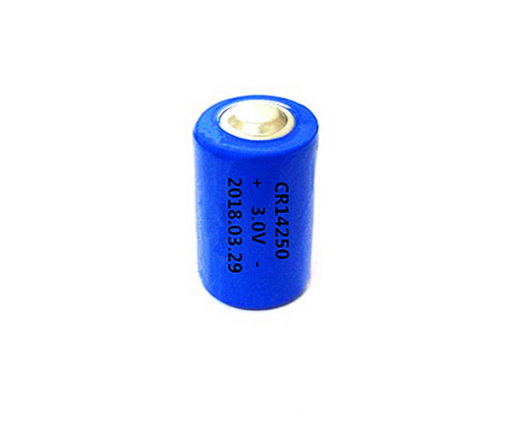

Primary lithium batteries are often mistaken for rechargeable lithium-ion (Li-ion) cells, but they serve a different purpose. These single-use, disposable lithium-metal batteries use lithium as the anode and a variety of materials for the cathode. Each chemistry offers unique advantages suited to specific applications.
Designed as a drop-in replacement for 1.5V alkaline AA and AAA batteries, Li-FeS₂ outperforms alkalines, especially in high-drain devices like digital cameras.
Higher operating voltage
Superior performance in cold temperatures
Low self-discharge rate, up to 15 years shelf life
Enhanced leak resistance
However, they are more expensive and have transportation restrictions due to safety regulations.
Known for high energy density and long life, Li-SOCl₂ batteries are used in military and industrial settings like oil and gas drilling.
Nominal voltage: 3.6V
Specific energy: 500 Wh/kg
Not suitable for high current draw
Used in: military fuses, medical equipment, remote sensors
Handling by trained personnel is essential due to their reactive chemistry.
Accounting for around 80% of global primary lithium battery usage, Li-MnO₂ is widely used in both consumer and industrial devices.
Nominal voltage: 3–3.3V
Energy density: ~280 Wh/kg
Supports both low-drain and pulse current applications
Used in: cameras, sensors, watches, CMOS batteries
Used mainly in defense applications, these batteries offer quick burst power and a decent shelf life of 5–10 years.
Nominal voltage: 2.8V
Energy density: ~330 Wh/kg
Formats: A, C, D
Used in: military gear, defibrillators
| Chemistry | Specific Energy (Wh/kg) | Voltage | Power Output | Passivation | Safety | Cost | Shelf Life | Operating Temp | Applications | Common Formats |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alkaline | 200 | 1.5V | Low | None | Good | Low | 10 years | 0°C to 60°C | Consumer devices | AA, AAA, C, D, 9V, coin |
| Li-FeS₂ | 300 | 1.5V | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Affordable | 15 years | 0°C to 60°C | High-drain electronics | AA, AAA |
| Li-SOCl₂ | 500 | 3.6–3.9V | Excellent | Moderate | Requires caution | Industrial-grade | 10–20 years | -55°C to 85°C+ | Fracking, military | Cylindrical, cuboid |
| Li-MnO₂ | 280 | 3–3.3V | Moderate | Moderate | Good | Affordable | 10–20 years | -30°C to 60°C | Sensors, cameras | AA, C, D, coin, cuboid |
| Li-SO₂ | 330 | 2.8V | Moderate | Moderate | Requires caution | Industrial-grade | 5–10 years | -54°C to 71°C | Defense, defibrillators | A, C, D |
While rechargeable batteries dominate many modern applications, primary lithium batteries remain irreplaceable where long shelf life, high energy density, and extreme reliability are required. Understanding the differences among Li-FeS₂, Li-SOCl₂, Li-MnO₂, and Li-SO₂ chemistries enables better battery selection across consumer, industrial, and military domains.
 Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4700mAh 3.6V Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V
Nickel Cadmium Nicd Battery Pack SC1800mAh 3.6V Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack D4000mAh 3.6V Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V
Ni-Cd Battery Pack C2500mAh 3.6V NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V
NICAD Battery Pack AA900mAh 3.6V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 3.2V LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V
LiFePO4 IFR18650 1600mAh 6.4V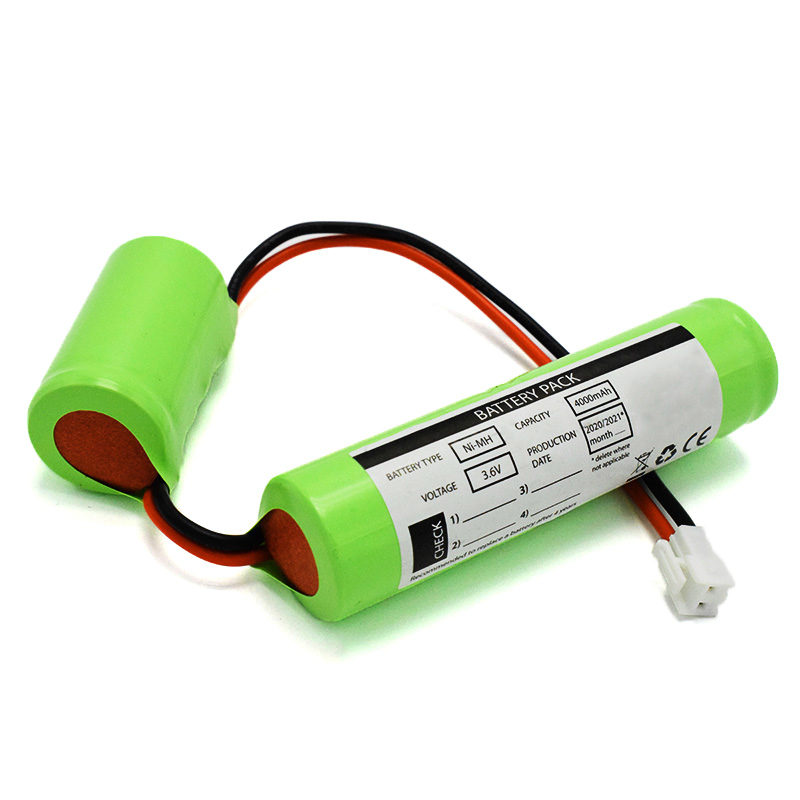 Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V
Ni-MH Battery C4000mAh 3.6V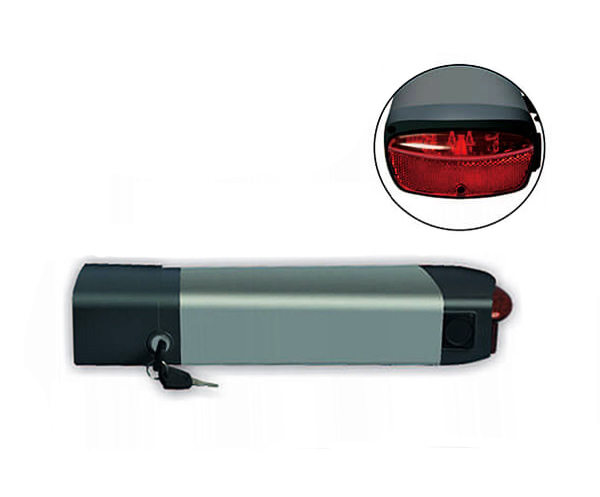 E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1
E-bike Battery 48V 10Ah JL-1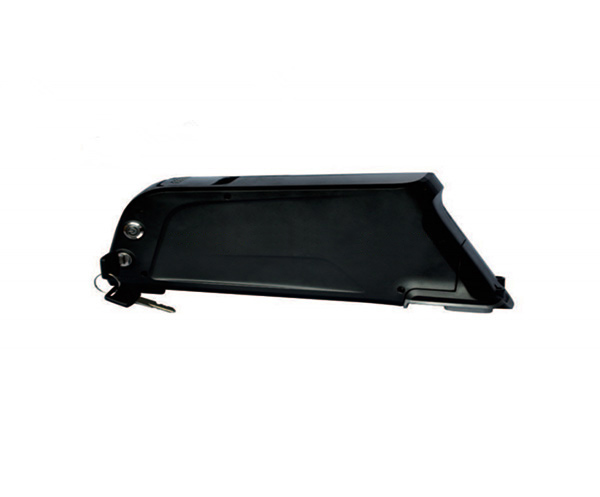 E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian
E-bike battery 48V 10Ah Qing Tian